Fire Detection System – Types, Working, Installation & Maintenance Guide
Updated: 15-Aug-2025
119
A fire detection system is an essential safety mechanism designed to detect smoke, heat, or flames early to prevent property damage and loss of life. Modern fire detection systems are widely used in homes, offices, factories, and public spaces, integrating with fire suppression systems to provide rapid emergency responses. From residential fire detection systems to complex industrial fire detection systems, these setups ensure that any fire incident detection occurs promptly, triggering alarms and alerts for evacuation or suppression.
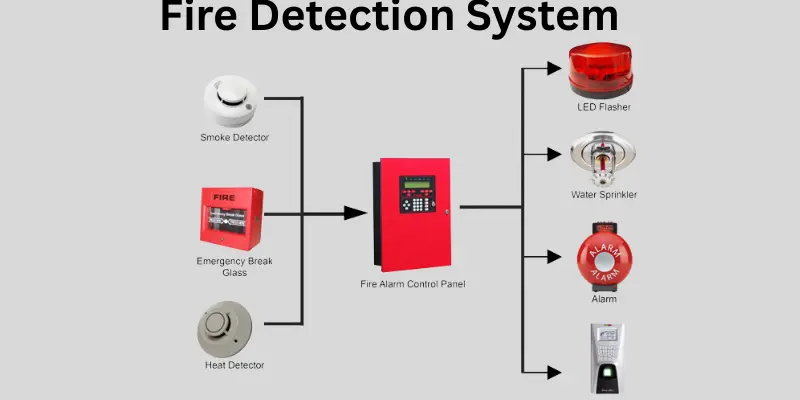
Table of content to choice your topic
What is a Fire Detection System?
A fire detection system is an integrated arrangement of fire detection equipment that monitors for signs of fire, such as smoke, temperature changes, or gas levels, and alerts occupants through alarms. They are categorized into automatic fire detection systems and manual systems, depending on activation methods.
Types of Fire Detectors
Different types of fire detectors are used depending on the environment and risk level. The main fire detector types include:
- Heat Detectors – Trigger when temperature exceeds a set limit.
- Smoke Detectors – Detect smoke particles using ionization or photoelectric sensors.
- Flame Detectors – Sense infrared or ultraviolet light emitted by flames.
- Gas Detectors – Identify harmful gases produced during combustion.
- Multi-Sensor Detectors – Combine smoke, heat, and gas sensors for advanced protection.
Different Types of Fire Detection Systems
The type of detectors used often defines the overall fire detection system setup. Common variations include:
- Conventional Fire Detection System – Uses fixed wiring zones; ideal for small properties.
- Addressable Fire Detection System – Identifies exact detector location; perfect for large buildings.
- Wireless Fire Detection System – Uses radio signals; faster to install and flexible.
- VESDA Fire Detection System – Very Early Smoke Detection Apparatus for sensitive environments.
- Fenwal Fire Detection System – High-performance detection for industrial and aviation applications.
- Honeywell Fire Detection System – Known for reliability and smart integration.
Applications of Fire Detection Systems
Here’s more detail regarding application
Residential Fire Detection Systems
- Protect homes with home fire detection systems that integrate with smart devices.
Commercial Fire Detection Systems
- Offices, malls, and hotels rely on commercial fire detection systems for large-scale protection.
Industrial Fire Detection Systems
- Factories and plants use heavy-duty industrial fire detection systems to safeguard equipment and workers.
Hazard Detection Systems
- Specialized hazard detection systems are installed in chemical, oil, and gas facilities.
Fire Detection & Suppression Integration
A well-designed fire detection and alarm system often integrates with a fire suppression system (e.g., sprinklers, gas suppression) to automatically respond to detected threats.
Installation & Costs
Fire detection installation cost depends on:
- Size of premises
- Type of system (automatic fire detection system, addressable, wireless)
- Brand (VES fire detection systems, Honeywell, Fenwal)
- Compliance with safety regulations
Maintenance of Fire Detection Systems
Fire detector maintenance is crucial for reliability:
- Regular sensor cleaning
- Battery replacement for wireless fire detection systems
- Testing alarms monthly
- Professional inspections every 6–12 months
Training & Supplier Selection
Many fire detection system suppliers provide fire detection systems training to ensure correct use. Choose suppliers with certified products and after-sales support.
Industrial-Grade Fire Detection And Suppression Systems
Industrial-grade systems are designed for large-scale facilities such as factories, warehouses, oil refineries, and chemical plants. They combine advanced fire detection (smoke, heat, flame, and gas sensors) with fire suppression technologies (water mist, foam, gas-based agents, or dry chemicals).
- Key Features: Rugged construction, multi-zone monitoring, high sensitivity sensors, and integration with automated suppression.
- Applications: Heavy manufacturing, hazardous material storage, power plants.
- Benefit: Rapid detection and instant suppression to reduce downtime, loss, and risk to life.
Best Fire Detection System For Commercial Buildings
The best choice often depends on building size, occupancy, and risk profile. Addressable fire detection systems are ideal for commercial spaces because they can pinpoint the exact location of an alarm.
- Recommended System: Addressable system with smoke, heat, and flame detectors, integrated with voice evacuation and central monitoring.
- Benefits: Quick response, minimal false alarms, efficient evacuation guidance.
Smart Fire Detection Systems For Homes
Smart systems use Wi-Fi-enabled smoke and heat detectors that send alerts to smartphones and integrate with smart home assistants.
- Features: Mobile notifications, remote monitoring, self-testing, battery status alerts.
- Benefits: Peace of mind while away from home, better false alarm control, and integration with other smart devices (e.g., unlocking doors for firefighters).
Fire Detection System Installation Requirements
Installation must comply with local building codes and NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) or relevant international standards.
- Requirements:
- Fire risk assessment before installation
- Proper detector placement (per manufacturer guidelines)
- Use of certified components
- Power supply redundancy (main + backup battery)
- Trained technicians for installation and commissioning
Difference Between Smoke And Heat Detectors
- Smoke Detectors: Detect particles from combustion using optical (photoelectric) or ionization technology; best for early warning.
- Heat Detectors: Trigger when temperature exceeds a preset limit or rises rapidly; better for high-dust or smoky industrial environments.
- Main Difference: Smoke detectors react to fire in the incipient stage, while heat detectors respond in later stages.
Benefits Of An Addressable Fire Detection System
- Pinpoints exact detector location
- Easier maintenance and troubleshooting
- Reduces false alarms
- Supports large, complex layouts
- Integrates with HVAC and access control systems
Fire Detection System Maintenance Checklist
- Test alarm sounders and strobes
- Inspect detectors for dust or obstruction
- Check battery backup and power supply
- Verify control panel indicators
- Simulate alarms to check response time
- Document maintenance activities
Wireless Vs Wired Fire Detection Systems
- Wired Systems: More reliable, no battery replacement needed, ideal for new builds.
- Wireless Systems: Easier to install in existing buildings, flexible layout changes, but require periodic battery replacement.
- Choice: Depends on building structure, budget, and future expansion needs.
Fire Detection System Testing Procedure
- Notify building occupants and monitoring stations before testing
- Use test smoke/heat to trigger detectors
- Verify panel receives correct signals
- Check notification devices (sirens, strobes)
- Reset system and log results
Fire Detection Standards And Regulations
- NFPA 72: National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code
- ISO 7240: International standard for fire detection
- EN 54: European fire detection standard
Compliance ensures safety, legal adherence, and insurance eligibility.
Integration Of Fire Detection With Building Management Systems (BMS)
Modern fire detection systems can connect with BMS for automated responses:
- Shutting down HVAC to stop smoke spread
- Unlocking emergency exits
- Activating suppression systems
- Sending alerts to security teams
Advantages Of Early Fire Detection
- Saves lives by enabling timely evacuation
- Minimizes property damage
- Reduces business interruption
- Helps firefighters respond more effectively
- Lowers insurance premiums
Types Of Fire Detection Technologies
- Ionization Smoke Detectors – Good for fast-flaming fires
- Photoelectric Smoke Detectors – Good for smoldering fires
- Heat Detectors – Fixed temperature or rate-of-rise
- Flame Detectors – UV, IR, or combined sensors
- Gas Detectors – Detect combustion gases (CO, CO₂)
- Multi-Sensor Detectors – Combine smoke, heat, and gas sensing for higher accuracy
Top 10 Manufacturers Of Fire Detection Systems
Prices below are typical list/online ranges for single devices or small panels, not full projects. Enterprise systems are usually quoted. See notes after the table for source examples.
| Manufacturer (Key Brands) | Typical Usage | Typical Operation Duration* | Where To Use | Indicative Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Honeywell (Notifier, Fire-Lite, Gent, Morley, Xtralis/VESDA) | Addressable & conventional detection, aspirating (VESDA), full FACP suites | Detectors ~10 yrs; Panels 10–15 yrs | Commercial, industrial, data centers, campuses | Addressable detector $45–$120 (e.g., Notifier FSP-951); small panel $800–$3,000. |
| Siemens (Cerberus PRO) | Advanced addressable, multi-criteria detection, integration | Detectors ~10 yrs; Panels 10–15 yrs | Large commercial, healthcare, transportation | Multi-sensor detector $150–$220 (FDOOT271). |
| Johnson Controls (Simplex/Tyco) | Addressable networks, enterprise integration | Detectors ~10 yrs; Panels 10–15 yrs | Airports, hospitals, higher ed | UL 268 7th-ed compliant lines; typical detector $80–$200. |
| Edwards (EST/Kidde Commercial) | Addressable detection & notification | Detectors ~10 yrs; Panels 10–15 yrs | Commercial, institutional | Edwards SIGA-OSD optical ~$100–$160 (varies by distributor). |
| Bosch (Avenar) | Addressable & video/fire integration, multi-sensor | Detectors ~10 yrs; Panels 10–15 yrs | Offices, logistics, retail | Optical detector $70–$130 (e.g., FAP-425 series). |
| Eaton (Cooper/Menvier) | EN54 addressable & emergency lighting | Detectors ~10 yrs; Panels 10–15 yrs | Europe/ME commercial & industrial | Addressable detector $60–$120 (EN54 market, distributor dependent). |
| Hochiki | Global EN54/UL addressable & conventional | Detectors ~10 yrs; Panels 10–15 yrs | Industrial, warehousing, commercial | ALG-EN (addr. optical) often $40–$100 online. |
| Apollo Fire (Halma) | XP95/Discovery/Soteria lines | Detectors ~10 yrs; Panels 10–15 yrs | Commercial, marine (EN54/Marine) | XP95 optical $25–$60 (market dependent). |
| Securiton (SecuriSmoke ASD) | High-sensitivity aspirating detection | Detectors ~10 yrs; ASD units often 10–15 yrs | Data centers, museums, clean rooms | ASD units typically $2,000–$6,000+ depending on model. |
| Fike | Flame detectors, industrial fire & gas | Detectors 5–10 yrs typical; controllers 10–15 yrs | Oil & gas, heavy industry | Triple-IR flame detectors $1,500–$4,000+ (model dependent). |
* Most commercial smoke/heat detector heads are replaced around 10 years per manufacturer guidance & code practice; smoke alarms for dwellings are widely recommended at 10-year replacement.
Price source notes (examples): Online distributor pages for representative models (Siemens FDOOT271, Notifier FSP-951, Securiton ASD units, Apollo XP95, Bosch FAP-425), plus market notes on Simplex UL-268 7th-ed detectors. Ranges vary by region and integrator.
International Standards & Guidelines Governing Fire Detection
Global / Cross-Market
- ISO 7240 series — Fire detection and alarm systems (design, components, performance). Widely harmonized globally. NFPA
- EN 54 series — EU/UK baseline for components & systems (detectors, panels, power, etc.).
- UL 268 (Smoke Detectors for Fire Alarm Systems), UL 521 (Heat Detectors) — U.S. product standards referenced by NFPA 72.
- NFPA 72 — National Fire Alarm & Signaling Code (installation, testing, maintenance, documentation). Adopted/Referenced by U.S. building & fire codes.
Hazardous Areas (Oil & Gas / Chemical / Dust)
- IEC 60079 / IECEx & ATEX 2014/34/EU for equipment in potentially explosive atmospheres. (Marking, conformity routes.) Certification Management LimitedInternal Market SMEsEUR-Lex
Sectors / Occupancies
- Healthcare (US): NFPA 99 (Health Care Facilities Code) interfaces with NFPA 72 for fire alarm in medical occupancies.
- Data Centers / IT & Telecom: NFPA 75 (IT Equipment) & NFPA 76 (Telecom) for detection/suppression design coordination.
- Aviation Hangars: NFPA 409 defines hangar groups & fire protection/detection requirements.
- Road Tunnels/Bridges: NFPA 502 (detection & life safety in tunnels/bridges).
- Marine/Offshore: SOLAS Ch. II-2 & IMO FSS Code Ch. 9 mandate shipboard fire detection & testing.
- UK/Europe Installations: BS 5839 (application & design guidance) alongside EN 54 product standards.
International Statistics: Losses Due To Ineffective Use Of Fire Detection
- Homes without alarms or with alarms that failed account for the majority of deaths. NFPA notes “roughly 3 out of 5” home fire deaths happen where no smoke alarms or no working smoke alarms were present.
- Risk reduction when alarms actually work: The death rate per 1,000 home fires is ~55–60% lower when working smoke alarms are present.
- Global burden: CTIF’s World Fire Statistics report (No. 30, 2023) across 49–80 reporting countries shows ~3.8 million fires/year with ~26,000 civilian fire deaths/year—underscoring the scale where detection & response gaps drive losses.
- U.S. 2023 snapshot: NFPA’s national fire loss series shows $48.9B in direct property loss (all fires), emphasizing the economic impact where detection/response is inadequate.
Interpretation: “Ineffective use” covers no system, disabled devices, expired sensors, lack of maintenance/testing, or poor coverage—all repeatedly identified in NFPA/USFA analyses of fatal incidents.
International Statistics: Achievements Due To Effective Fire Detection
- Life safety benefit: Working smoke alarms cut the risk of dying in a reported home fire by ≈55–60% (NFPA).
- Property loss mitigation: USFA’s historic review shows fires with operable alarms contributed a disproportionately small share of property loss versus fires without alarms or with failed alarms.
- Trend improvements: NFPA’s national time-series reports show long-term reductions in incidents and stabilizing fatality rates when modern codes (e.g., UL 268 7th ed nuisance-resistant detectors) and regular maintenance/testing are adopted.
Operating Mechanism Chart (With Respect To Temperature)
Major detector types relate to temperature and time (fixed-temperature thresholds vs. rate-of-rise criteria). Smoke detectors are not temperature-driven; they trigger on smoke obscuration/particles.
Rule-of-thumb references: Common fixed-temperature ratings: ~57°C, 68°C, 79°C, 93°C; rate-of-rise activation typically around ≥6.7°C/min (≈12°F/min); smoke detectors follow UL 268 performance/nuisance-resistance criteria (not temperature setpoints).
Quick sourcing notes (clickable):
- NFPA 72, 75, 409, 502; NFPA research & fire loss statistics.
- ISO 7240, EN 54/BS 5839.
- UL 268 & UL 521 (smoke/heat detectors, latest editions & context).
- ATEX / IECEx & hazardous area guidance.
- CTIF World Fire Statistics (global burden).
- Representative pricing pages (examples) for Siemens, Notifier/Honeywell, Apollo, Bosch, Securiton.
Summary
A fire detection system is an essential safety investment for homes, offices, and industries. With various types of fire detectors and systems available—from conventional fire detection systems to addressable fire detection systems—the right choice depends on the application, budget, and safety needs. Proper installation, integration with suppression, and regular maintenance ensure maximum protection against fire hazards.
Conclusion
Whether it’s a residential fire detection system or a complex industrial fire detection system, timely detection saves lives and property. With options like VESDA fire detection systems, Honeywell fire detection systems, and Fenwal fire detection systems, there is a solution for every environment. Combining detection with suppression, and ensuring regular maintenance, guarantees the system performs effectively in emergencies.

FAQs
1. What is the best fire detection system for homes?
For homes, wireless fire detection systems or smart-enabled smoke detectors are ideal due to easy installation and remote alerts.
2. How does an automatic fire detection system work?
It senses smoke, heat, or flames using sensors, automatically triggering alarms and often activating the fire suppression system.
3. What is the difference between conventional and addressable fire detection systems?
Conventional systems divide buildings into zones, while addressable systems pinpoint the exact location of the triggered detector.
4. How much does fire detection installation cost?
It varies from $500 for small home fire detection systems to several thousand for commercial fire detection systems, depending on size and type.
5. How often should fire detectors be maintained?
Monthly testing and professional servicing every 6–12 months ensure system reliability.
6. Are wireless fire detection systems reliable?
Yes, modern wireless fire detection systems are highly reliable, using encrypted signals and battery backups.
Please Write Your Comments